Welcome to Suzhou Sincere Enterprise Management Consulting Co.!
Contact number:400-8606560


Current position:Home > Learning Programs > Enterprise Internal Training > Internal Training Courses
The operation and development of the enterprise is a series of problem-solving process, the effect of problem solving will directly determine the effectiveness of the enterprise;
Problem solving is not solely rely on experience, not to mention by shooting the brain, a flash of insight to solve, must need a set of methods that can be replicated within the organization to get good use of good promotion;
For professionals, in the process of successfully and excellently completing a job, will always encounter big or small problems. Without mastering the method of analyzing and solving work problems, it is a hindrance to the work itself. Many managers are often puzzled by the following problems:
How do you throw off the fog on the surface of a problem and discover what it is?
How to change old habits of inertia and impulsive problem solving?
How to analyze and solve problems with systems thinking and solve problems efficiently with limited resources?
The ability to analyze and solve problems has become one of the basic competencies necessary for professionals, especially managers.
1. to help business people to recognize problems, identify causes, find countermeasures and implement actions in the work process;
2. to clarify the ideas of analyzing problems and solving problems;
3. to master the methods and steps of problem analysis;
4. to master the principles, methods and strategies of problem solving;
5. to improve individual and team problem-solving skills and team decision-making ability;
6. work more quickly and effectively as a team and as individuals with complex or simple problems, decisions, and planning;
7. resolving incidents of concern and clarifying misinformation on the basis of facts (not guesses or assumptions);
8. identifying the real reasons for poor or good performance and determining solutions and improvements;
9. implement solutions and improvements more effectively through excellent risk management.
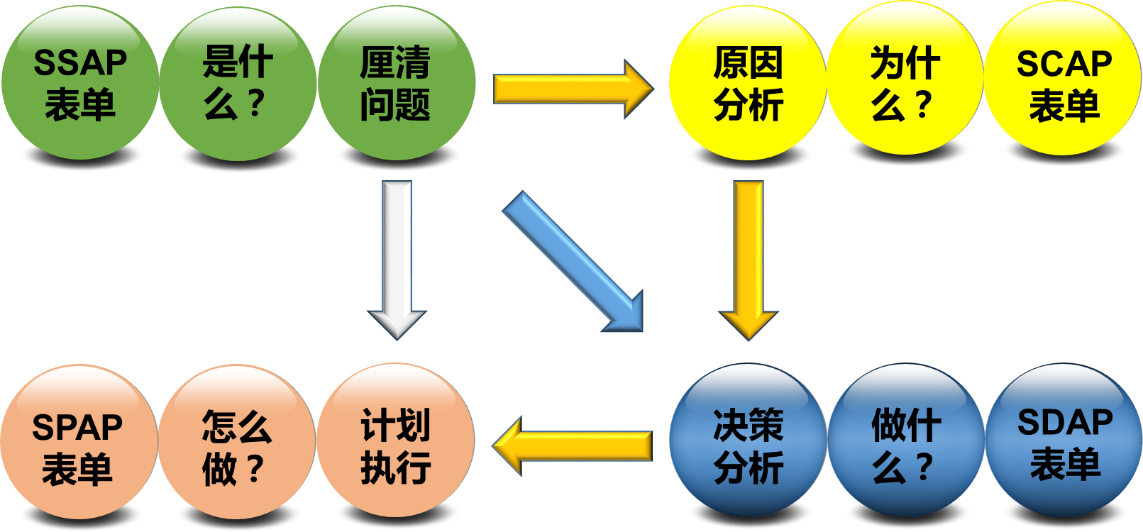
Course Topics (First level of catalog) | Training Topics (Secondary Catalog) | Time of instruction | Teaching Methods |
Clarify the problem: Recognizing the nature of the problem is the starting point for fundamental problem solving. | Global Game: Harvest Season The fundamental purpose of clarification is to "get the facts right", and the main steps are: 1. Describe the problem Principles for describing the problem 2. Concretizing the problem 5W1H method Samsara (name) Principles and checklists for issue refinement 3. Sorting the issues Principles of problem sequencing Urgency, significance, trends 4. Decide on a starting point for analysis cause analysis approach Decision-making Program analysis | 3.0H | Classroom Lectures Case Study Practical exercises Role play
Outputs: SSAP form |
Cause analysis: Knowing the reason for not knowing the reason is not able to solve the problem, must recognize the reason why the problem occurs in order to truly and accurately solve the problem. | The fundamental purpose of cause analysis is to "find out why things happen", and the main steps are: 1. Description of the problem Describe the ten dimensions of the problem 2. Finding and comparing comparators Finding the right comparison 3. Looking for clues Finding clues to the problem Criteria and deviations 4. Inferring probable cause Brainstorming (pioneering method) Troubleshooting (Trial & Error) Fishbone Diagram (Problem & Criteria) Method Common sense analysis method (expert method) Logical Flaw Method (Comparative Method) Logical Conditions, Logical Relationships, Logical Consequences Logical Relationships - Deduction, Inference, Extrapolation 5. Examine the probable cause 6. Verify probable cause Expert method sample verification method … | 4.0H | Classroom Lectures Case Study Practical exercises
Outputs: SCAP forms |
Decision Analysis. Making decisions is the situation we face the most in our daily work and life, often not without a solution, but with a multitude of answers to choose from. | The fundamental purpose of decision making is to "make sound decisions" and the main steps are: 1. Describe the objectives of the decision SMART approach to goal setting 2. Setting decision-making criteria restrictive condition Elements of expectation weights 3. Identifying options brainstorming method Osborne checklist method preference matrix 4. Conducting risk assessments likelihood of significance Risk assessment matrix Acquisition of support | 3.0H | Classroom Lectures Case Study Practical exercises
Outputs: SDAP forms |
Plan for implementation: Good decisions must be accompanied by good planning and execution to solve problems. | The fundamental purpose of program analysis is to "ensure that the program is fully implemented and continuously improved", and the main steps are.: 1. Describe the goals of the program Break down the plan into 6 elements of action 2. Develop action steps and identify critical links 3. Identify potential problems 4. Develop preventive and contingency measures | 3.0H | Classroom Lectures Case Study Practical exercises
Outputs: SPAP form |
Problem analysis and resolution summary and practice | Problem analysis and solution must be to solve the actual problem, through the actual exercise of the actual problem of the enterprise, and combined with the lecturer's comments, proficiency in problem analysis and solution methodology process. | 1.0H | classroom teaching |